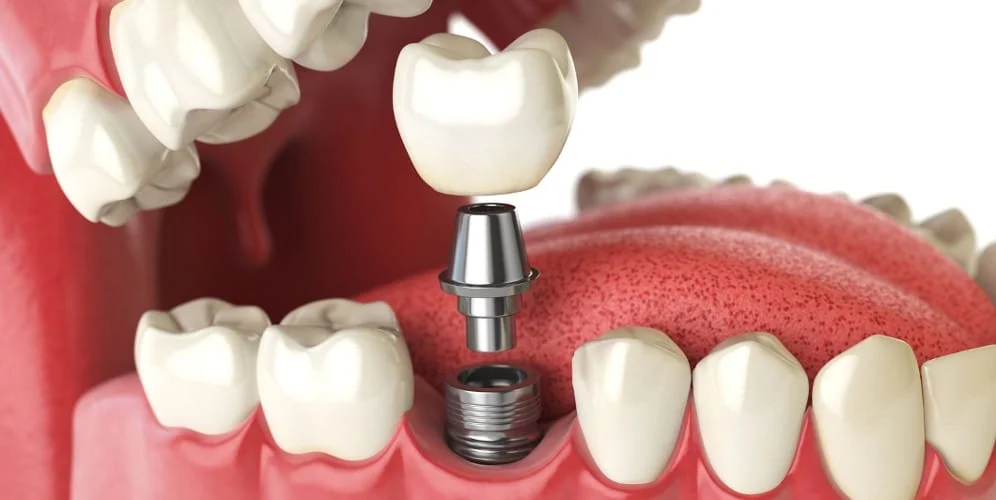
Integration of Bone and Titanium in Dental Implants
Bone and titanium fusion in dental implants
In the world of dental restoration, dental implants are emerging as a revolutionary solution to replace missing teeth.
Behind the success of dental implants lies a remarkable process of osseointegration,
where the bone integrates seamlessly with the implant material, especially titanium.
This article delves into the complex mechanism of how bone is implanted in dental procedures involving titanium implants.
1. Dental implants:
Dental implants are artificial tooth roots that are surgically placed in the jawbone to support a replacement tooth or bridge.
They are made of biocompatible materials,
with titanium being the most widely used due to its excellent properties such as strength,
durability, and compatibility with the body’s tissues.
2. The importance of osseointegration
Osseointegration is the biological process in which living bone fuses with the surface of the implant,
essentially holding it firmly in place.
This integration ensures the stability and function of dental implants,
mimicking the function of a natural tooth root.
3. Titanium:
Ideal planting material
Titanium has unique properties that make it an ideal choice for dental implants.
Its biocompatibility ensures minimal risk of rejection by the body’s immune system.
Furthermore,
titanium’s ability to form a strong bond with bone facilitates osseointegration,
providing a solid foundation for artificial teeth.
4. Osseointegration process
-
Initial healing:
- After the implant is placed,
the healing process begins with the formation of a blood clot around the implant site.
Over time, the clot is replaced by granulation tissue,
paving the way for bone regeneration. -
Bone formation:
- Osteocytes, specialized cells that form bone,
migrate to the surface of the implant and begin depositing new bone tissue.
This gradual formation of bone around the implant causes it to fuse with the surrounding bone structure -
Maturity stage:
- As osseointegration progresses, the newly formed bone matures and remodels,
enhancing the stability and strength of the implant over time
5. Factors affecting osseointegration
There are several factors that can affect the success of osseointegration, including
-
Implant design:
- Implant design,
including its surface properties and geometry,
plays a critical role in promoting osseointegration. -
Bone quality:
- The density and quality of the surrounding
bone affects the rate and extent of osseointegration -
Surgical technique:
- Careful surgical techniques, such as proper implant placement and appropriate bone preparation,
are essential to achieve optimal osseointegration
6. Promoting skeletal integration
-
Surface modifications:
- Surface treatments, such as acid etching or sandblasting,
can enhance the surface roughness of the implant,
promoting better adhesion and osseointegration. - Bone grafting:
- In cases where bone volume is insufficient, bone grafting procedures may be performed to increase bone around the implant site, facilitating osseointegration.